As the sprint planning progresses, it is essential to remain adaptable and responsive to the evolving needs of the project. This involves revisiting the sprint backlog, updating the sprint burndown chart, and addressing any risks or impediments that may arise.
By embracing a flexible approach, teams can ensure that the sprint remains on track and that the project goals are ultimately achieved.
Sprint Planning Overview
Sprint planning is a critical part of the Scrum process. It is an opportunity for the team to come together and plan the work for the upcoming sprint. During sprint planning, the team will define the scope of the sprint, identify the tasks that need to be completed, and estimate the time and resources required.The
sprint planning process typically begins with a review of the product backlog. The product backlog is a list of all the work that needs to be done on the product. The team will then select the items from the product backlog that they will work on during the upcoming sprint.Once
the team has selected the items for the sprint, they will begin to break them down into smaller tasks. Each task should be small enough that it can be completed within a single sprint. The team will then estimate the size of each task using story points.
Story points are a relative measure of the size of a task. They are used to help the team prioritize the tasks and to track progress during the sprint.After the team has estimated the size of each task, they will create a sprint backlog.
The sprint backlog is a list of all the tasks that the team will work on during the sprint. The sprint backlog is used to track the progress of the sprint and to identify any risks or impediments.
As the Sprint Planning Progresses
As the sprint planning progresses, the team may need to revise the sprint backlog. This can happen if the team discovers that they have underestimated the size of a task or if they encounter any unexpected risks or impediments. The team should also update the sprint burndown chart as the sprint progresses.
The sprint burndown chart is a graphical representation of the amount of work that has been completed during the sprint. It is used to help the team track their progress and to identify any potential problems.In addition to revising the sprint backlog and updating the sprint burndown chart, the team should also identify and address any risks or impediments.
Risks are events that could potentially prevent the team from completing the sprint. Impediments are obstacles that are preventing the team from making progress. The team should develop strategies to mitigate risks and remove impediments.
Refinement and Estimation

During sprint planning, the team will often need to refine user stories. User stories are brief descriptions of the features that the team will be building during the sprint. The team may need to refine user stories to make them more specific or to break them down into smaller tasks.The
team will also need to estimate the size of each task. The team can use a variety of techniques to estimate the size of tasks, such as story points, t-shirt sizes, or ideal days. The team should choose a technique that they are comfortable with and that is appropriate for the size of the project.
Sprint Goal and Scope: As The Sprint Planning Progresses
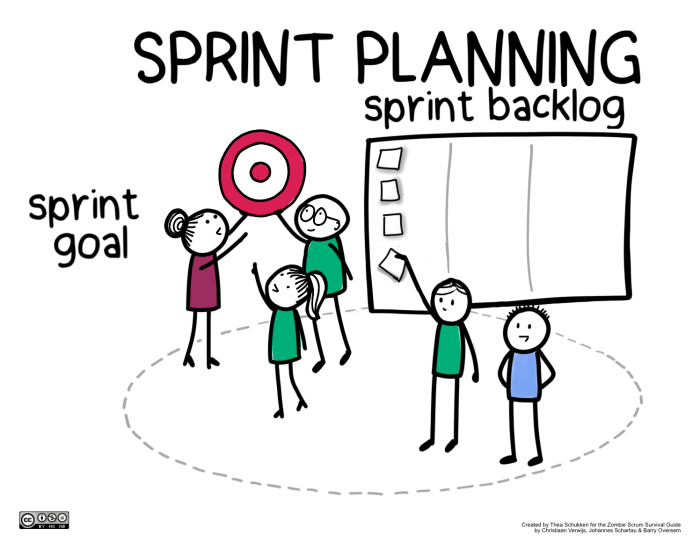
The sprint goal is a statement that describes the overall objective of the sprint. The sprint goal should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. The sprint scope is the list of all the work that the team will complete during the sprint.
The sprint scope should be aligned with the sprint goal and should be achievable within the time frame of the sprint.
Sprint Backlog Management
The sprint backlog is a list of all the tasks that the team will work on during the sprint. The sprint backlog is managed by the team and is updated as the sprint progresses. The team should add and remove tasks from the sprint backlog as needed.
The team should also re-estimate tasks as needed. The team should track the progress of the sprint backlog and identify any risks or impediments.
Communication and Collaboration
Communication and collaboration are essential for successful sprint planning. The team should communicate the sprint plan to the stakeholders. The team should also collaborate with the stakeholders to track progress and resolve issues. The team should hold daily stand-up meetings to discuss progress and identify any blockers.
Essential FAQs
What is the purpose of revising the sprint backlog as the sprint planning progresses?
Revising the sprint backlog allows teams to adapt to changing requirements and priorities, ensuring that the sprint remains aligned with the project goals.
How does the sprint burndown chart help in tracking the progress of the sprint?
The sprint burndown chart provides a visual representation of the remaining work, helping teams to identify potential bottlenecks and adjust their plans accordingly.
What are some common risks or impediments that may arise during the sprint planning process?
Common risks or impediments include unrealistic estimates, lack of resources, and changes in requirements. Teams should proactively identify and address these issues to minimize their impact on the sprint.