Gizmo distance time and velocity time graphs – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of motion analysis with gizmo distance-time and velocity-time graphs. These powerful tools provide invaluable insights into the intricate dynamics of objects in motion, empowering us to unravel the mysteries of speed, displacement, and time.
Distance-time graphs chronicle the evolution of an object’s position over time, while velocity-time graphs capture the variations in its velocity. Together, they paint a comprehensive picture of an object’s motion, enabling us to determine its speed, direction, and acceleration.
Distance-Time Graphs: Gizmo Distance Time And Velocity Time Graphs
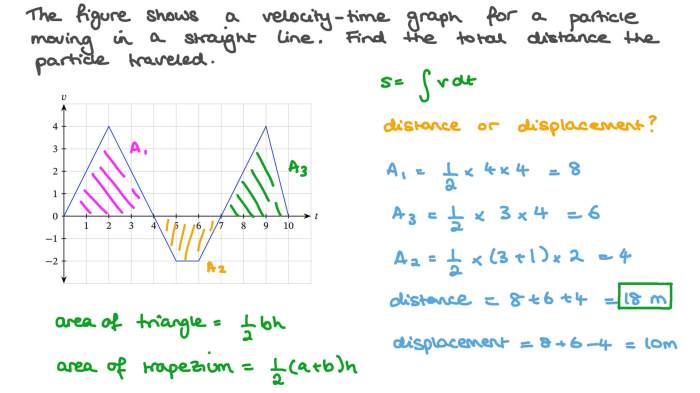
A distance-time graph is a graphical representation of the distance traveled by an object over time. It is a useful tool for analyzing the motion of an object, as it allows us to visualize the object’s speed and acceleration.
A distance-time graph is typically a straight line, with the distance traveled plotted on the y-axis and the time elapsed plotted on the x-axis. The slope of the line represents the object’s velocity, which is the rate at which the object is traveling.
If the slope of the line is positive, the object is moving in a positive direction (away from the origin). If the slope is negative, the object is moving in a negative direction (towards the origin). If the slope is zero, the object is not moving.
Velocity-Time Graphs
A velocity-time graph is a graphical representation of the velocity of an object over time. It is a useful tool for analyzing the motion of an object, as it allows us to visualize the object’s acceleration.
A velocity-time graph is typically a straight line, with the velocity plotted on the y-axis and the time elapsed plotted on the x-axis. The slope of the line represents the object’s acceleration, which is the rate at which the object’s velocity is changing.
If the slope of the line is positive, the object is accelerating in a positive direction (its velocity is increasing). If the slope is negative, the object is accelerating in a negative direction (its velocity is decreasing). If the slope is zero, the object is not accelerating.
Relationship between Distance-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs
Distance-time and velocity-time graphs are closely related. The slope of a distance-time graph represents the object’s velocity, and the area under a velocity-time graph represents the object’s displacement.
To convert a distance-time graph into a velocity-time graph, we simply need to calculate the slope of the line at each point. To convert a velocity-time graph into a distance-time graph, we need to integrate the area under the curve.
Applications of Distance-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs, Gizmo distance time and velocity time graphs
Distance-time and velocity-time graphs are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Analyzing the motion of objects
- Solving problems related to motion
- Designing and controlling machines
Query Resolution
What is the difference between a distance-time graph and a velocity-time graph?
A distance-time graph plots the distance traveled by an object against time, while a velocity-time graph plots the velocity of an object against time.
How can I determine the velocity of an object from a distance-time graph?
The slope of a distance-time graph represents the velocity of the object.
What is the area under a velocity-time graph?
The area under a velocity-time graph represents the displacement of the object.