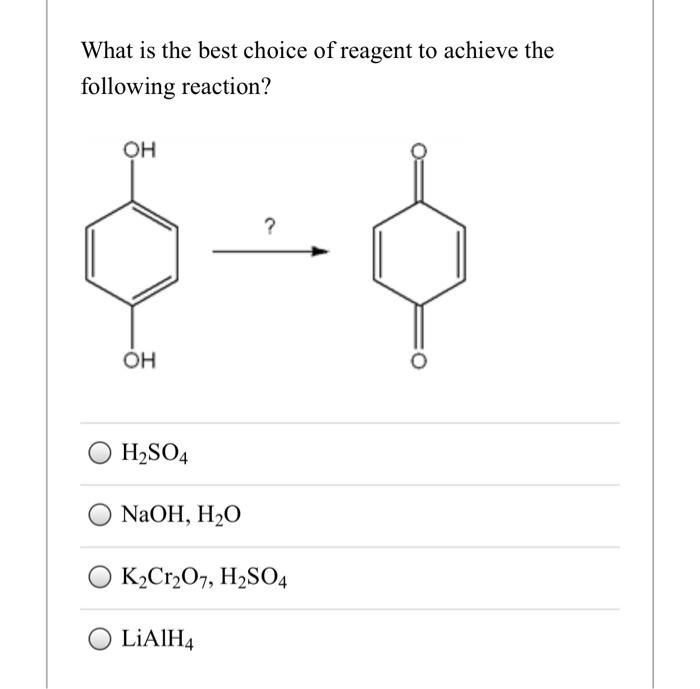
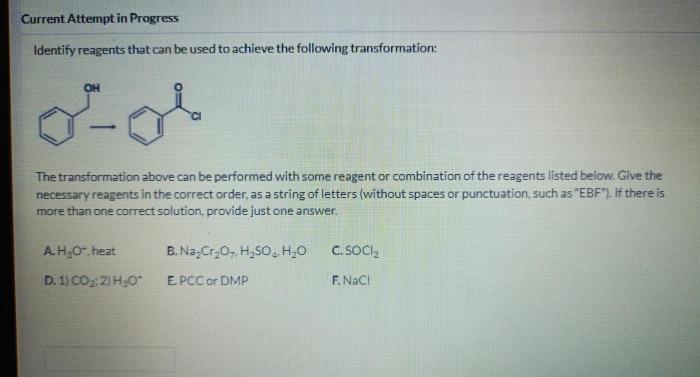
Select the best reagents to achieve the following transformation: – In the realm of organic synthesis, selecting the best reagents is paramount to achieving desired transformations efficiently and effectively. This article delves into the intricacies of reagent selection, providing a comprehensive guide to navigate the complexities of chemical reactions.
Understanding the type of transformation, desired product, and starting materials is crucial. Key factors to consider in reagent selection include functional group reactivity, regio- and stereoselectivity, solvent effects, and green chemistry principles.
Reagent Selection for Organic Transformations: Select The Best Reagents To Achieve The Following Transformation:
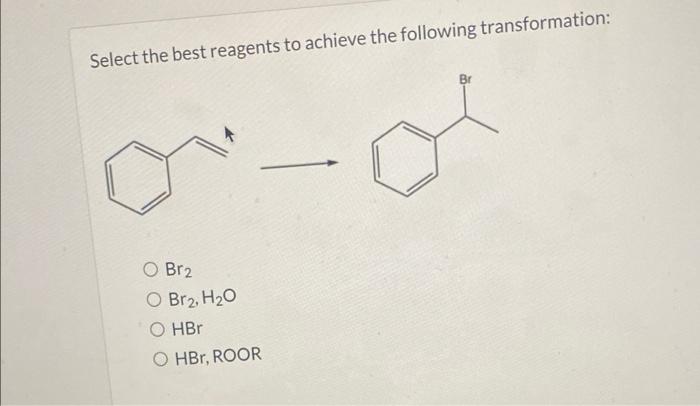
Organic transformations are fundamental reactions in organic chemistry, enabling the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler starting materials. Selecting the appropriate reagents is crucial for achieving the desired product efficiently and selectively.
Overview of Transformation Reaction, Select the best reagents to achieve the following transformation:
Transformation reactions involve the conversion of one functional group into another. The type of transformation depends on the specific functional groups involved and the desired outcome. Common transformation reactions include nucleophilic substitution, electrophilic addition, and oxidation-reduction reactions.
Reagent Selection Criteria
The selection of reagents for a transformation reaction depends on several key factors:
-
-*Reactivity of the functional groups
Different functional groups exhibit varying reactivity towards different reagents. For example, alkenes are more reactive towards electrophilic reagents than alkanes.
-*Steric and electronic effects
The steric and electronic environment around the functional group can influence the reactivity of the reagent. Bulky substituents or electron-withdrawing groups can hinder or enhance reactivity.
Common Reagents for Different Transformations
The following table lists common reagents for different types of transformation reactions:
| Transformation Type | Reagent 1 | Reagent 2 | Example Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleophilic Substitution | Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) | Alkyl halide (R-X) | R-X + NaOH → R-OH + NaX |
| Electrophilic Addition | Hydrogen bromide (HBr) | Alkene (R-CH=CH2) | R-CH=CH2 + HBr → R-CHBr-CH3 |
| Oxidation-Reduction | Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) | Alkene (R-CH=CH2) | R-CH=CH2 + KMnO4 → R-COOH + MnO2 |
Regio- and Stereoselectivity
Regio- and stereoselectivity are important considerations in reagent selection. Regioselectivity refers to the preference for a particular reaction site, while stereoselectivity refers to the preference for a particular stereoisomer. Different reagents can exhibit different regio- and stereoselectivities, which can affect the outcome of the reaction.
Solvent Effects
Solvents can influence the outcome of a reaction by solvating the reactants and products, thereby affecting their reactivity and selectivity. Polar solvents favor ionic reactions, while nonpolar solvents favor nonpolar reactions.
Green Chemistry Considerations
Green chemistry principles should be considered when selecting reagents. Environmentally friendly reagents and reaction conditions minimize waste and reduce the impact on the environment.
Practical Considerations
Practical considerations such as cost, availability, and safety should also be taken into account when selecting reagents. The choice of reagents should be appropriate for the specific laboratory setting and resources available.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors to consider when selecting reagents?
Functional group reactivity, regio- and stereoselectivity, solvent effects, and green chemistry principles are essential factors to evaluate.
How can regio- and stereoselectivity affect the outcome of a reaction?
Different reagents can influence the regio- and stereochemistry of the product, leading to variations in molecular structure and properties.
Why is it important to consider green chemistry principles in reagent selection?
Green chemistry aims to minimize environmental impact. Selecting environmentally friendly reagents and reaction conditions reduces waste and promotes sustainability.